|
Dinar
-
Exchange |
"Invest in your future - Invest in the Dinar!"
|
|
|---|
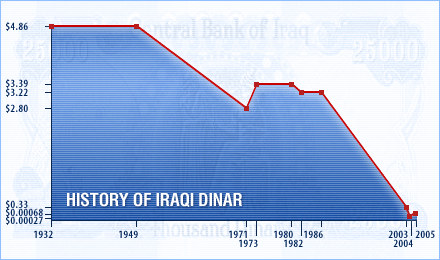 The Iraqi dinar was worth $3.20 before the United Nations embargo that followed Iraq's 1990 invasion of Kuwait. By August 2002 it was trading at just below 2000 to the US dollar, and by mid-April 2003 it had slipped to anywhere between 3500 and 4000 against the dollar. In July 2003 one US dollar equaled about 1,500 Iraqi dinars. Nearly all the bank notes issued after the 1991 Gulf War were without watermark or metal line due to technical difficulties, hich is why so many forgeries took place.
The Iraqi dinar was worth $3.20 before the United Nations embargo that followed Iraq's 1990 invasion of Kuwait. By August 2002 it was trading at just below 2000 to the US dollar, and by mid-April 2003 it had slipped to anywhere between 3500 and 4000 against the dollar. In July 2003 one US dollar equaled about 1,500 Iraqi dinars. Nearly all the bank notes issued after the 1991 Gulf War were without watermark or metal line due to technical difficulties, hich is why so many forgeries took place.
In April 2003, following the end of major combat operations, the Iraqi economy was in distress because of closure of oil sales, imposition of UN sanctions. At that time, United States officials said that a new currency was needed, to introduce some stability. Without a proper currency in circulation there was a fear of inflation. The US decided to distribute $20 bills to the civil servents to boost the economy. This was not an issue of "dollarizing" the economy, but to get money that had real value into people's hands.
As Brad Setser, former acting director of the US Treasury Office of International Monetary Policy, noted, "A currency that is tightly linked to the dollar would ... make it harder for the government of Iraq to manage its dependence on oil revenues. The dollar revenue from oil sales is highly volatile, so the government would have trouble paying the same dollar salary when oil is at $10 a barrel and when oil is at $30 a barrel. Rather than matching expenses and revenues by paying dollar salaries that vary in line with global oil prices, it is far easier to pay salaries in a local currency and let the value of the local currency fluctuate against the dollar."
By the end of April 2003 the economic life and conditions in Kirkuk city were becoming increasingly difficult due to the severe shortage of fuel, the increase in market prices and the non-payment of salaries to the civil servants in Kirkuk. The produce in the market had become increasingly expensive due to the significant rise in the number of people from Erbil and Sulaymaniyah who traveled to Kirkuk for shopping purposes. These shopping trips by people from the northern governorates were a result of the more attractive prices at which products were available in Kirkuk compared to the north, due to the low value of the 'new' Iraqi Dinar used in Government of Iraq [GOI] areas as against the 'old' Iraqi Dinar in use in the north.
In the long run, Washington wanted a new Iraqi government to pick its own currency, much as Afghanistan adopted a new one after the fall of the Taliban. As of May 2003 the US reportedly estimated that it was unlikely that a new government would be formed in Iraq in less than a year, and it would take at least three months after that to design a new currency. Until then, the Iraqis would have to use the various currencies floating in the market.
In June 2003 the Iraqi central bank once again began printing Dinars, with fallen leader Saddam Hussein's image on them. The 250 dinar denominated banknotes were printed by the Baghdad mint, under the supervision of the manager of the central bank. This was an effort to overcome a severe shortage of Iraqi dinars and to offset fears of counterfeit currency.
The administrator for the Coalition Provisional Authority in Iraq, Paul Bremer, outlined in an address to the Iraqi people, in July 2003, on the key spending priorities for the Iraqi national budget over the coming six months. These included commitments to improve the water, electrical, public health and telecommunications systems.
Bremer announced that the Coalition would print and distribute new banknotes for Iraq. In response to this press announcement in Baghdad, De La Rue confirmed that it was in discussions to assist in the production of banknotes for Iraq. The Company led a consortium of global currency specialists to manufacture the banknotes. De La Rue is the world's largest commercial security printer and papermaker, involved in the production of over 150 national currencies and a wide range of security documents such as travellers cheques and vouchers. Thomas de la Rue began printing British postage stamps in 1855, and obtained the contract for all Indian postal requirements.
Banknote Corporation of America, Inc. (BCA) is the largest high security printer in the United States, with headquarters in New York City and a manufacturing plant in North Carolina. Banknote Corporation specializes in intaglio printing, producing stamps for the United States Postal Service as well as for foreign postal administrations.
Bremer stated that the so-called "print" dinars in circulation in most of Iraq, nor the formal national currency (or "Swiss" dinar) still used in some parts of the Kurdish North were suitable for the new Iraq. "Print dinars" are poor quality, and in practice circulate widely in only two denominations -- the 250 dinar note, and the 10,000 dinar note [and no coins]. This made Saddam dinar notes very inconvenient to use. The "Swiss" dinars, while of higher quality, were so old that they are literally falling apart in people's hands. The former national ("Swiss") dinar notes were used throughout Iraq until the early 1990's, and this national currency still circulates in the Kurdish north. The bills nicknamed “Swiss dinar” either because of their relative stability and strength or because it was made in Europe, depending on the account. The Swiss dinar was trading at about 6.7 to the dollar in early July 2003.
Bremer stated that a new currency had not been designed by the United States as only a sovereign Iraqi government could take that decision. The new currency would not depict Saddam Hussein. The design for the new currency, which was not been released in advance to the public, was taken from the designs of the "Swiss" dinar, though the new notes will have different colors and denominations. The new dinars will be printed in a full range of denominations: in 50s; 250s; 1,000s; 5,000s; 10,000s; and 25,000s. The new banknotes will be much better protected against counterfeiting, they will be much more durable and suffer less "wear and tear".

The new currency would be made available to the Iraqi people on October 15, 2003. They will replace the existing Iraqi "print" dinars at parity: one new Iraqi dinar will be worth the same as one "print" dinar. The new dinar will replace the "Swiss" dinar at the rate of 150 new dinars to one Swiss dinar. These different rates reflect the different prices, expressed in local currency, in different parts of the country.
Currency can be exchanged at branches of the Rafidain and Rasheed banks, and Iraqis would have three months in which to make the exchanges. On August 18, 2003 the Central Bank of Iraq advised Iraqis to deposit all their dinars in local banks to facilitate their change into the new currency. The Bank's governor, Faleh Dawood Salman, said the UK firm charged with printing the new Iraqi money intended to ferry the first shipments to the country in a few days. "The process of changing the money has started and I call on all Iraqis to open accounts in both government and private banks and deposit the amounts they are willing to swap," Salman said. On October 1, 2003 it was disclosed that agents from the Defense Criminal Investigative Service (DCIS) and the 812th Military Police Company assisted by Iraqi police and the Ministry of Finance had broken a counterfeit printing operation in Baghdad and seized counterfeit currency worth 100 billion dinars. DCIS agents and Military Police raided two locations, seized printing presses and arrested Amar Fadil Ramadan Al-Kayse, an Iraqi national who was subsequently released to Iraqi Ministry of Interior officials for prosecutorial action by the Iraqi Ministry of Justice and Courts. The investigation leading to the arrest of Al-Kayse revealed that Al-Kayse was printing and attempting to pass counterfeit 250 Iraqi dinar notes to the Central Bank of Iraq (CBI), which is funded and operated by the Coalition Provisional Authority (CPA). Al-Kayse owned and operated the Sarmad Company for Printing, a local Baghdad printing shop and worked as editor of Nuktat Dhaw (“Spot Light”), a newspaper in Baghdad.
Stephen Cecchetti, Professor of International Economics and Finance at Brandeis University, noted in June 2003 that "Cultural legitimacy is the final and most important issue to confront in designing the new Central Bank of Iraqi. What any of foreigners write or say is irrelevant unless the people of Iraq are involved. Most importantly, we cannot go into Iraq and build a set of institutions that reflect American and Western European values. This will not work. The new Central Bank of Iraqi will belong to the Iraqis and so they have to set it up. While I might think it would be fitting to start printing new Iraqi currency with an image of King Hammurabi on it, I’m not going to use the currency."
The new currency was unveiled during a press conference in the capital of Baghdad, October 4, 2003. Iraq's new banknotes include pictures of an ancient Babylonian ruler and a 10th century mathematician in place of the face of Saddam Hussein. An ancient Islamic compass, patterned on an Astrolabe from Baghdad dated 1131 AD, on the new Iraqi 250 dinar banknote replaced the face of Saddam Hussein on the old note. This is the same Arabic Astrolabe that was used on the ˝ dinar note of the 1980s issue and the 1000 Dinar note of the 2002 issue.
Copyright © 2005 - Dinar-Exchange.com
 The Iraqi dinar was worth $3.20 before the United Nations embargo that followed Iraq's 1990 invasion of Kuwait. By August 2002 it was trading at just below 2000 to the US dollar, and by mid-April 2003 it had slipped to anywhere between 3500 and 4000 against the dollar. In July 2003 one US dollar equaled about 1,500 Iraqi dinars. Nearly all the bank notes issued after the 1991 Gulf War were without watermark or metal line due to technical difficulties, hich is why so many forgeries took place.
The Iraqi dinar was worth $3.20 before the United Nations embargo that followed Iraq's 1990 invasion of Kuwait. By August 2002 it was trading at just below 2000 to the US dollar, and by mid-April 2003 it had slipped to anywhere between 3500 and 4000 against the dollar. In July 2003 one US dollar equaled about 1,500 Iraqi dinars. Nearly all the bank notes issued after the 1991 Gulf War were without watermark or metal line due to technical difficulties, hich is why so many forgeries took place.
